NPTEL Social Networks Week 9 Assignment Answers 2025
1. A dataset follows a power-law distribuon if:
- A small number of observaons dominate the total sum.
- The data is symmetric and bell-shaped.
- The probability of extreme values is negligible.
- The distribuon always has a finite upper bound.
Answer :- For Answers Click Here
2. Which of the following functions best represents a power-law probability distribution?
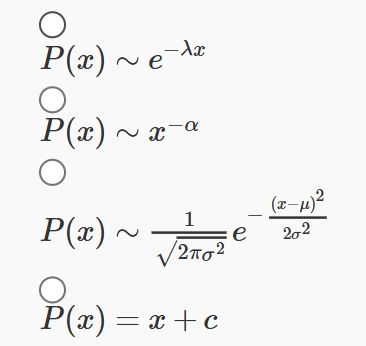
Answer :-
3. Why do normal distributions commonly appear in natural and social systems?
- They result from the accumulation of small independent random variables.
- They always represent financial systems.
- They arise when data is generated from a single source.
- They only appear in symmetric datasets.
Answer :-
4. If a process follows a normal distribution rather than a power law, which characteristic is not expected?
- Long-tailed distribution
- A well-defined mean and standard deviation
- Symmetry around the mean
- Predictable probability intervals
Answer :-
5. The degree distribution of the World Wide Web (WWW) follows a power-law. What does this imply?
- A small number of websites (hubs) have extremely high connectivity, while most have very few links.
- All websites have approximately the same number of links.
- Websites are connected randomly without any preference for linking.
- The WWW graph follows a normal distribution.
Answer :- For Answers Click Here
6. In a power-law degree distribution of the web graph, what happens when a new page is created?
- It is equally likely to link to any existing page.
- It has a higher probability of linking to a highly connected (popular) page.
- It is more likely to link to a randomly chosen low-degree page.
- It distributes links in a Gaussian manner.
Answer :-
7. How can you verify whether a dataset follows a power-law distribution?
- Plot the frequency distribution on a log-log scale and check for a straight-line pattern.
- Compute the mean and standard deviation.
- Fit a normal distribution curve and check for symmetry.
- Apply the Central Limit Theorem.
Answer :-
8. The “Rich-Get-Richer” mechanism is an example of:
- Random attachment
- Preferential attachment
- Normal distribution of links
- Gaussian selection
Answer :-
9. The Barabási-Albert model generates networks that:
- Follow a uniform degree distribution
- Are scale-free and exhibit power-law degree distribution
- Have equal probability of linking to any node
- Have constant node degrees over time
Answer :-
10. What happens when high-degree nodes are removed from a scale-free network compared to a random network?
- A scale-free network collapses rapidly, while a random network degrades gradually.
- Both networks show similar behavior.
- A random network collapses faster.
- A scale-free network becomes more resilient.
Answer :- For Answers Click Here


